With the increasing reliance on electronic devices, having a stable source of electricity is more important than ever before. In fact, power outages and fluctuations can damage your appliances or even cause data loss. To mitigate these risks, most people rely on an inverter to protect their devices from voltage spikes, and keep their homes running when the power goes out. But how exactly does an inverter work, and what benefits does it provide?
What is an Inverter?
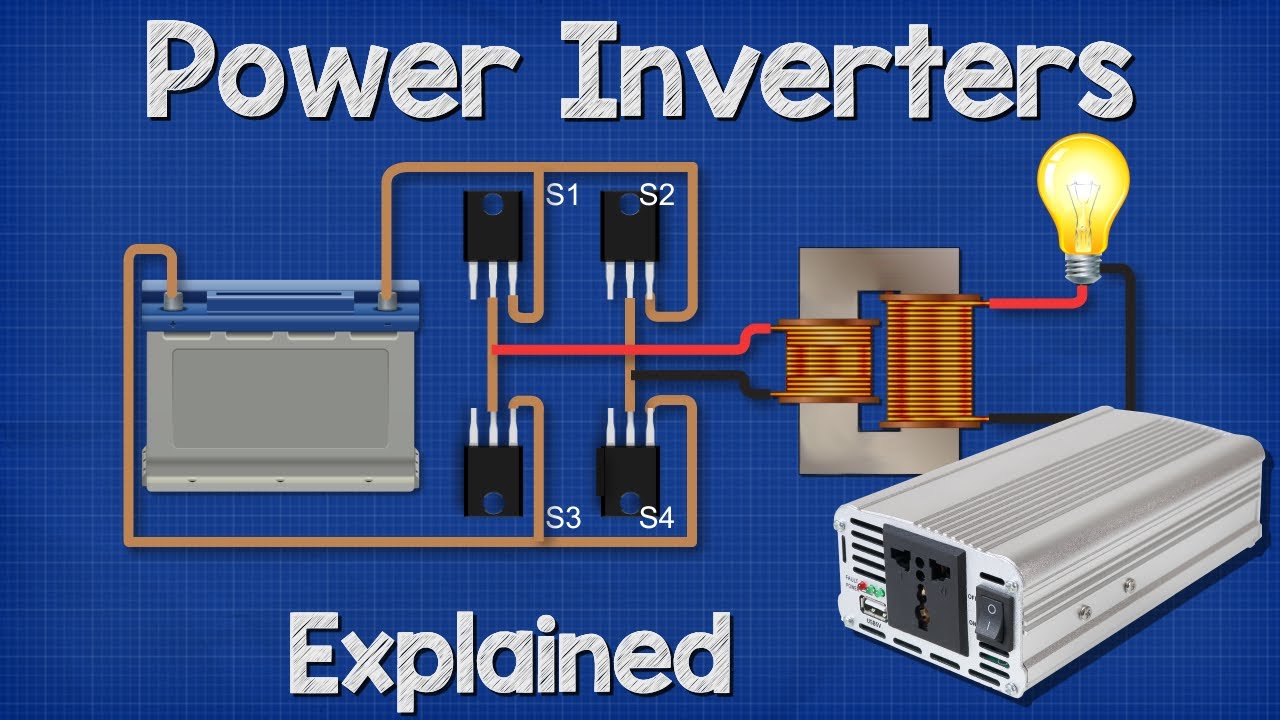
An inverter is a device that converts DC (direct current) electricity into AC (alternating current) electricity, either for backup power or for use in devices that run on AC power. In essence, an inverter "inverts" or changes the electrical current, allowing devices to use the required electricity type.
Types of Inverters
There are two main types of inverters:
- Standby Inverter: A standby inverter is typically used as a backup power source for homes during power outages. It's connected to a battery that stores DC electricity, which is then converted into AC power when needed.
- Grid-Tie Inverter: A grid-tie inverter is used in homes that draw electricity from the grid, but it also allows any excess energy generated by solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable sources to be sent back to the grid.
How Does an Inverter Work?
The basic working principle of an inverter is simple: it converts DC electricity into AC electricity. However, the process involved is more complex than it sounds. Here are the basic steps involved when an inverter is turned on:
- The inverter takes DC electricity from a battery or other source.
- The direct current is passed through a circuit that contains multiple components, including transformers, capacitors, and transistors.
- These components work together to block one half of the sine wave produced by AC power. This results in a waveform that's similar to AC power, but with a flat top and bottom.
- The waveform that's produced is modified by varying the voltage and frequency. This ensures that the output mimics AC power almost perfectly.
- The modified sine wave is then passed through a transformer, which boosts the voltage to an appropriate level for the devices it will power.
- Finally, the AC power is distributed through circuits and outlets, where it can be used to power a variety of devices, from lights to appliances and other electronics.
Benefits of Inverters in Homes
There are a number of benefits to installing an inverter in your home, including:
- Backup Power: As mentioned earlier, an inverter can provide backup power during outages, ensuring you can still use appliances and stay connected to the internet.
- Prevents Data Loss: Sudden power loss or fluctuations can cause data loss on electronic devices. An inverter helps prevent this issue by providing stable power at all times.
- Energy Efficiency: Depending on the type of inverter you install, you can improve the energy efficiency of your home, save money, and reduce your carbon footprint by tapping into renewable energy sources.
Conclusion
Through its ability to convert DC electricity to AC power, an inverter is an important device that can serve as a backup power source or even provide energy from renewable sources for homeowners. Whether you're interested in backup power or want to reduce your carbon footprint, consider installing an inverter in your home.